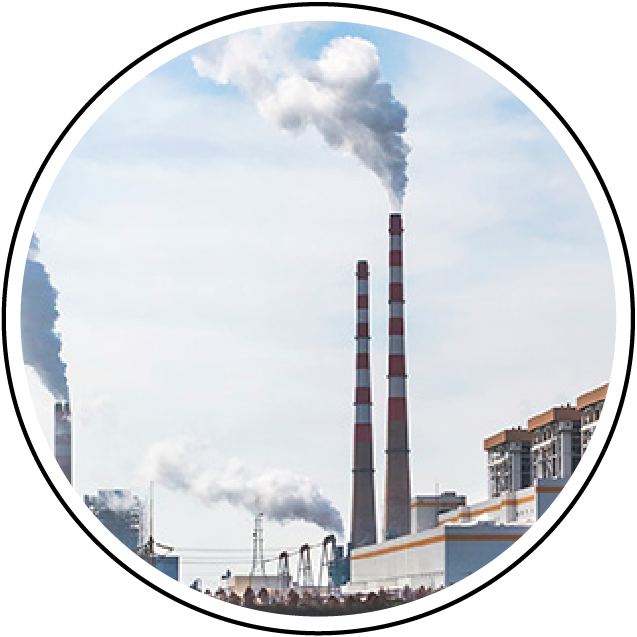

Stack Emission
Monitoring in Dubai
Stack emission monitoring is the process of measuring and analyzing the pollutants released into the atmosphere from industrial stacks or chimneys. This monitoring is crucial for ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and minimizing the harmful effects of emissions on air quality and public health. Industries such as power plants, refineries, cement factories and chemical manufacturing facilities use stack monitoring to assess the types and concentrations of pollutants they emit.
Key pollutants monitored during stack emission analysis include sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2). These emissions can contribute to environmental issues such as acid rain, smog and climate change as well as health problems like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
Stack emission monitoring involves the use of continuous emission monitoring systems (CEMS), which provide real-time data on the concentration of pollutants. In some cases, manual sampling and analysis are performed to verify the the accuracy of
automated systems. The data gathered helps industries meet regulatory standards, identify inefficiencies and adopt cleaner technologies.
Effective stack emission monitoring supports environmental protection efforts, reduces the risk of air pollution and ensures that industrial operations align with sustainable practices and emission limits set by government agencies.
Source of emission: Diesel generator, paint booth, Industrial stack emission and boiler etc.
Area of Stack, Ambient Temperature, Flue Gas Temperature, Flue Gas Pressure, Flue Gas Velocity, Volume of Gas discharged (Flow Rate),Total Suspended Particles (TSP), Sulphur Dioxide (SO2), Nitric Oxide (NO), Oxides of Nitrogen (DNOx),(Expressed as Nitrogen dioxide NO2),Carbon Monoxide (CO),Carbon dioxide (DCO2),Oxygen (O2),Hydrocarbons (HC).
Limits: The Standard Limits taken from UAE Federal Law Cabinet Decree (12) 2006. Annexure-2 &1.
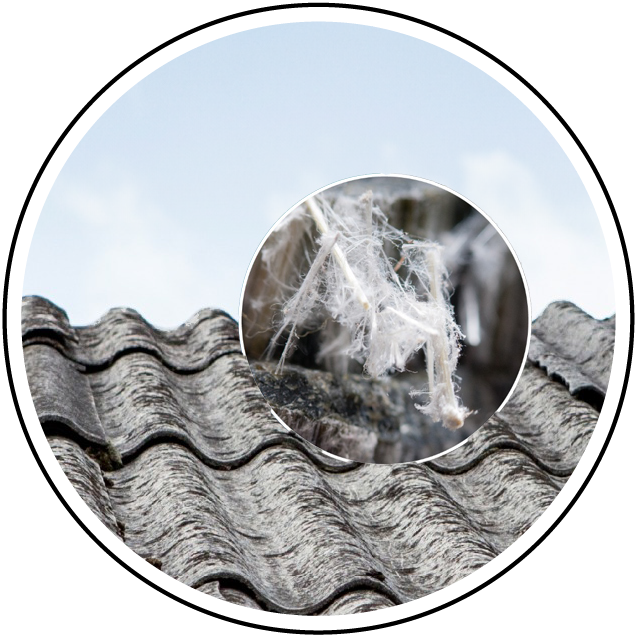


Asbestos
Testing in Dubai
Asbestos analysis is the process of identifying and measuring the presence of asbestos fibers in materials or air samples. Asbestos a group of naturally occurring minerals was once widely used in construction and manufacturing due to its heat resistance, durability and insulating properties. However, it has been linked to serious health issues, including lung cancer, asbestosis, and mesothelioma, prompting strict regulations on its use and removal.
Asbestos analysis is essential in environments where asbestos-containing materials (ACMs) are suspected such as older buildings, insulation, roofing and flooring materials. The analysis can be conducted through bulk sampling, air testing or surface testing to detect airborne fibers that may pose a health risk during renovation or demolition activities.
Specialized techniques, such as polarized light microscopy (PLM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and phase contrast microscopy (PCM), are commonly used for asbestos detection and quantification. These methods help determine
whether asbestos is present, and if so, in what concentration ensuring that proper safety measures are implemented.
Asbestos analysis is critical in ensuring the safe management, removal or containment of asbestos, protecting workers and occupants from exposure. Compliance with asbestos regulations helps prevent long-term health risks, making the process a key component of building safety and public health protection.
Solid sample analysis as per US EPA 600.
Air sample analysis as per NIOSH 7400.


